HEALTH ENTERS THE AGENDA AT COP28, BUT THERE IS STILL MUCH TO DO
At COP28, health entered the agenda of the United Nations’ climate conferences for the first time. The COP28 Presidency and the World... Read More
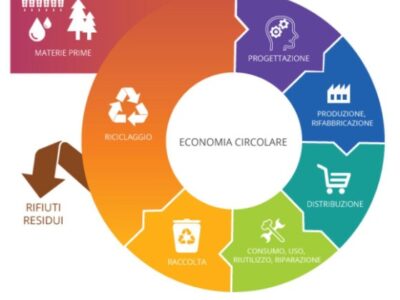
THE CIRCULAR ECONOMY IN THE CONTEXT OF FOOD SYSTEMS
The concept of the circular economy (CE) represents a development model that aims to mitigate the negative impacts of human actions through the implementation of the basic principles of the '3Rs': reduce, reuse and recycle, with the goal of constantly maintaining the highest degree of utility and value for products, components and materials. The basic principle, therefore, of the circular economy is the creation of economic value for those products that until now have been regarded as industry waste.
FOOD SYSTEMS AND CLIMATE CHANGE: STRATEGIES FOR TRANSITIONING TOWARDS SUSTAINABLE SOLUTIONS
Food systems consist of all the actors and activities involved in the production, aggregation, processing, distribution, consumption, and disposal of food products originating from agriculture, forestry, fisheries, food industries, and the economic, societal, social, and natural sectors involved.The concept described above emphasizes the scale and complexity of these systems, which involve the entire food chain and are central to human needs. However, while it is intuitive to consider food systems as essential for human life, it is less immediate to identify the interdependence between climate and food systems.
CULTIVATED MEAT: A Possible Measure for Climate Change Adaptation and Mitigation
Cultured meat (or "cultured meat") is a type of meat that is produced through the methodology known as "cellular agriculture." Cellular agriculture aims to produce food, including meat, fish and dairy products, from the cultivation of stem cells. The first key difference from conventional meat production is that cultured meat does not require animal farming. In fact, the main innovation of cultured meat is that it is not strictly necessary to grow one or more animals to obtain meat, but that it is possible to grow cells to obtain only the tissues needed for food.
CLIMATE MOBILITY AND MENTAL HEALTH CAUSES AND CHALLENGES
Climate change also has very different impacts on people's lives depending on the latitude in which they live. Several hundred thousand people are forced to move temporarily or permanently because their usual places of residence are no longer liveable.